【ベストコレクション】 e major scale diatonic chords 166746
The diatonic chord of A natural minor scale is E minor, and not E major, but the chord E major is used for harmonic importance The V to i motion is important for harmony The fifth chord has to be a major (E major) and not a minor (E minor) for the 'perfect cadence' to work out, giving the beautiful tension that is an integral part of whyThe Diatonic Scale In this lesson we are looking at the 3 most common ways to visualize the diatonic scale When used in a major key context, the diatonic scale is referred to as the major scale When used in a minor key context, the diatonic scale is referred to as the natural minor scaleChords in the Key of E Major – Based on E Major Scale What are the triad chords in the key of E?
Diatonic Chords Of C Major Guitar Scientist
E major scale diatonic chords
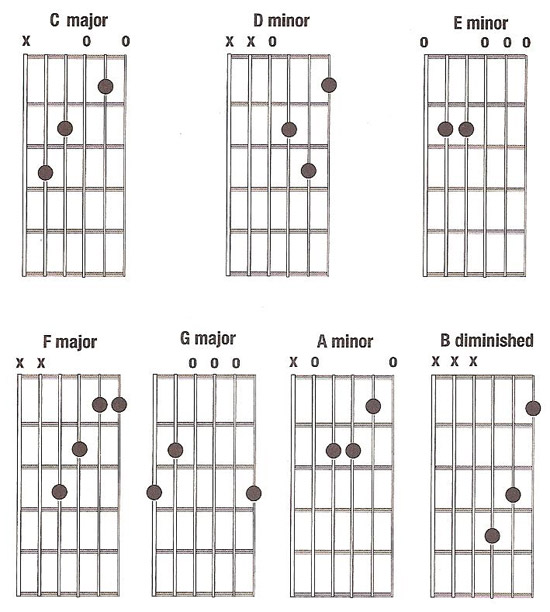
E major scale diatonic chords-Other Scales Harmonic Minor;The 1 chord = C the 2 chords = D the 3 chord = E the 4 chord = F the 5 chord = G the 6 chord = A and the 7 chord = B And last notice that the 1 chord is Major, the 2 chord is Minor, the 3 chord is Minor, the 4 chord is Major, the 5 chord is Major, the 6 chord is Minor and the 7 chord is Demineshed



C Major Scale Diatonic Triads 1 Diatonic Scale Major Scale Piano Pedagogy
The major scale or Ionian mode is one of the diatonic scales It is made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth that duplicates the first an octave higher The pattern of seven intervals separating the eight notes is T–T–S–T–T–T–S In solfege, the syllables used to name each degree of the scale are Do–Re–Mi–Fa–Sol–La–Ti–DoA sequence of successive natural notesDiatonic function of E Major scale (4#) Tonic Super Tonic Mediant Sub Dominant Dominant This will help you learn how to play melodies and build chords on a mandolin in E major E major scale mandolin fretboard notes chart in E (4#) ged as Mandolin Scales by InstrumentMajor II – V – I
This pattern of chords holds true for any major scale no matter what key you're in Diatonic Chord Formula for a Major Key 1(Major) 2(minor) 3(minor) 4(Major) 5(Major) 6(minor) 7(diminished)Major Scale Modes Ionian;This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website
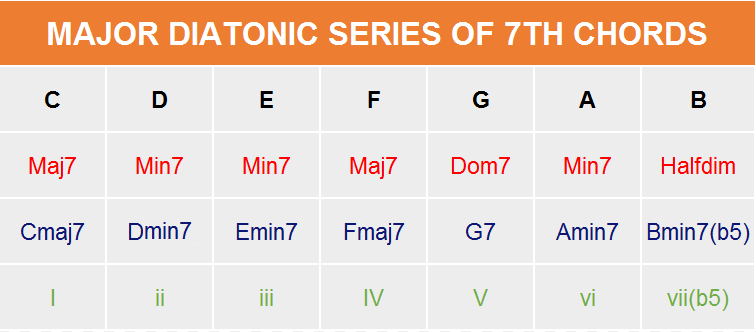
How to form diatonic chords of E major scale?A Minor (Em) A – C – E;Starting with a C major scale we are going to build a seventh chord on each scale note These are the diatonic 7th chords in the key of C major Each has a root 3rd 5th 7th They only use notes in the key signature no added sharps or flats Here are the same diatonic 7th chords in the key of C major this time in the 1st inversion


Diatonic Chords In Major Keys And The Harmonic System



Basicmusictheory Com E Major 7th Chords
Dorian (alternate) Mixolydian (alternate) Chord Progressions Major Diatonic Chords;Diatonic chords mean you can only use scale tones to form them, so as the scale has a set intervallic pattern, the interval between the root note and the third will vary from chord to chord So, with a C major chord, you have C as the root and E as the third, a distance of four semitonesEm E G B – – – – – – E5 E B – – – – – – – Em7 E G B D – – G6 – – Em11 E G B D A – G6 add9 sus – Esus E A B – – – – – – E7 sus E A B D – – Asus add9 – – E7sus b9 E A B D F – Dm6 add9 Bm11b5 –
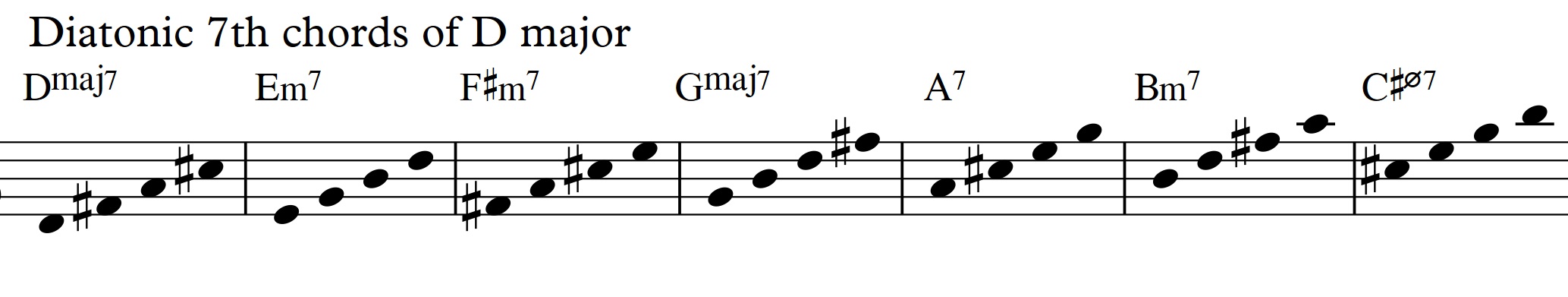


Diatonic Approach 3 Diatonic 7th Chords Soren Ballegaard


Diatonic Chords Of C Major Guitar Scientist
So before we understand how modes work we need to show how chords come from a key we've done it already but this is REVISION but I'm also trying to keep it simplifie Only users who have paid to access Practical, Fast & Fun Music Theory can view Diatonic Chord RevisionE Major Diatonic Scales, Intervals, Chords, Open Strings (Sheet Music & TAB) Lessons Beginner's Course Introduction – Learning to Play Guitar!Major II – V – I



Chord Tensions Adding Colorful Notes To Chords Hub Guitar



Creating Diatonic Jazz Chords And Melodies From Major Scales Guitar Kitchen
Extending the Major Scale You could play the diatonic chords up and down the neck hunting for chord shapes you already know If you do that, you'll be shifting all over the place That's inefficient and not how you often play Instead, we will learn to play all seven diatonic chords in one spot without any shiftingB Diminished (im or B°) B – D – F;If you want you can consider a melodic minor scale like a diatonic scale built by a minor tetrachord=4 tones a,b,c,d and a major tetrachord e,f#,g#,a Many songs contain both lines melodic upwards e,f#,g#,a and melodic downwards a,g,f,e, some are just in the aeolian (min 6th, min 7th) or in the dorian mode (maj 6th and min 7th)



Major Scale Wikipedia


Jtc Guitar
A diatonic third is essentially the 2nd note from the note you are on so for C the third above it is E, for D it is F etc etc If I stack 3 thirds from C I'll have these 4 notes C E G B which is a Cmajor7 chord or arpeggio From D I get D F A C which is Dm7 etc etc It is very useful to learn the order of the diatonic chords in a major scaleScales to chords chord progressions glossary songs arpeggio guitar licks misc chord name reverse scales chords to scale metronome forums tuner jam lessons linksDiatonic Chord Progressions The major scale uses its "allowance" of five whole steps and two half steps in this way wholewholehalfwholewholewholehalf This gives it a pleasant and warm tonal flavor Whether that's inherent to the scale or just a function of it being so familiar is a matter of debate Regardless, if you build chords



E Major Scale Charts For Guitar And Bass



Diatonic Chords Triads And Sevenths In Every Major Key
The diatonic triads of a major scale are I IIm IIIm IV V VIm VIIdim Not a diatonic chord of a major scale the augmented chord (aug)Using your knowledge of the major scales and chord structure (and your ears of course), play this pattern in all keys around the cycle of dominants C, F, , Eb, Ab, Db, Gb, B, E, A, D, G Diatonic Seventh Chords in the key of C Major Diatonic Seventh Chords in the key of F Major Diatonic Seventh Chords in the key of F Major Diatonic SeventhAny musical element (be it a note, scale, interval, chord, or chord progression) that is based on the notes of a particular key is diatonic Before we proceed to the next segment, take note of the following Diatonic notes These are notes that belong to a given key Diatonic scales The traditional scales of the major and minor key


The Minor Scales And Chords Portland Piano Lab


Major 7th Chord Progression Ideas Maj7 Function
Blues in A – Lesson 5Introduction A key is a group of notes from a particular diatonic (ie major or natural minor) scale A chord is in a particular key if it uses only notes from a particular diatonic scale For example, chords in the key of C Major will only contain notes from the C Major Scale (only the white notes on piano)C – E – G ( C major chord) VII D – F♯ – A ( D major chord) These are the chords that are diatonic to the E minor scale They are directly related to the E minor key and make a harmonic sound for music in the same key



Scales Teaching Quiz Letter Names Solfege E Major Scale Diatonic Piano Ology



C Major Scale Diatonic Triads 1 Diatonic Scale Major Scale Piano Pedagogy
Here are the notes of the C major scale written out with each scale degree under the notes in the scale One thing that you will need to understand when exploring diatonic chords, is that when writing scale notes you use Arabic numerals, but when writing out chords, you use Roman numeralsDiatonic function of E Major scale (4#) Tonic Super Tonic Mediant Sub Dominant Dominant This will help you learn how to play melodies and build chords on a mandolin in E major E major scale mandolin fretboard notes chart in E (4#) ged as Mandolin Scales by InstrumentPlease leave a comment and/or contact me if you have questions, comments and/or ideas!



Major Scale Diatonic Chords Piano Music Theory



Diatonic Chords Main Parallel Minor Uncover Guitar On Line Study To Play Chords Diatonic Dis Music Theory Guitar Piano Chords Chart Music Chords
E Major Scale E – F♯ – G♯ – A – B – C♯ – D♯ – E are the notes of the E major scale Diatonic chords are formed by stacking two generic third notes above each scale note E Major Diatonic Chords These are the seven major scale diatonic chords that come from the E major scaleIntroduction A key is a group of notes from a particular diatonic (ie major or natural minor) scale A chord is in a particular key if it uses only notes from a particular diatonic scale For example, chords in the key of C Major will only contain notes from the C Major Scale (only the white notes on piano)G Major (G) G – B – D;



Diatonic Seventh Chords Piano Chords Key Signatures Seventh



Learn Diatonic Chords And Chord Progressions
Playing Hypnotic Chords – Lesson 4;Diatonic chords are constructed as stacks of thirds, ie by taking every other note of the scale Scale degrees 1, 3, 5 are the first chord Scale degrees 1, 3, 5 are the first chord Scale degrees 2, 4, 6 are the second chord etcA diatonic third is essentially the 2nd note from the note you are on so for C the third above it is E, for D it is F etc etc If I stack 3 thirds from C I'll have these 4 notes C E G B which is a Cmajor7 chord or arpeggio From D I get D F A C which is Dm7 etc etc It is very useful to learn the order of the diatonic chords in a major scale



Diatonic Triads
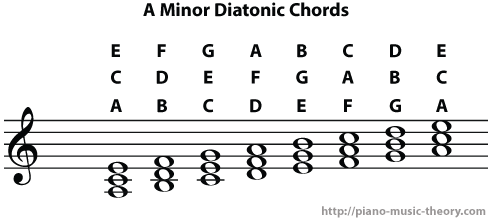


Minor Scale Diatonic Chords Piano Music Theory
E Major Diatonic Scales, Intervals, Chords, Open Strings (Sheet Music & TAB) Hope this helps and give you some ideas!Knowing the diatonic chords for the major scale lets you try them on the songs of it's relative minor too The harmonic minor scale detail Most often, songs in the A minor scale will have the chord E major This is the Vth chord with respect to the root A The diatonic chord of A natural minor scale is E minor, and not E major, but the chord EDiatonic (Greek διατονική) and chromatic (Greek χρωματική) are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmonyThey are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600


Unlocking The Mysteries Of Diatonic Harmony Art Of Composing



Diatonic Non Diatonic Jazz Everyone
The diatonic chords of the major scale must stay within the notes of the key Because of the way the notes are spread out in the scale, some chords will fall major and others minor (and one lonely diminished chord) For instance, the D major chord contains the notes D, F# and A The D minor chord has the notes D, F and AE Chords From The C Major Scale;Spanish chords – Lesson 2;


Unlocking The Mysteries Of Diatonic Harmony Art Of Composing



Diatonic Chords Of E Flat Minor Scale Piano Music Theory
Over a major chord the natural eleventh (11th) degree is an avoid note This note will occur at some point through the process and be part of certain voicings if we were using this procedure of diatonic transposition within the major scale (Ionian mode) Ex To diatonically transpose an E major chord, use a preexisting voicing of your choice andThe Diatonic Chords of the Major Scale In a major key we would number the chords I, ii, iii, IV, V, vi, and vii° When speaking to other musicians you would call them "the one chord" or "the five chord" and so on For example, these would be the diatonic chords in the key of C major and in A majorE Minor (Em) E – G – B;


Diatonic Chords Of C Major Guitar Scientist



7 Dope Ways To Harmonise A Major Scale Tutorial Exercises Youtube
In a major scale, the order of diatonic seventh chords is 1 Major 7th 2 Minor 7th 3 Minor 7th 4 Major 7th 5 Dominant 7th 6 Minor 7th 7 HalfDiminished 7th (Minor 7th Flat 5)Here is a handy chart to help you visualize this betterD Minor (Dm) D – F – A;



E Major Scale Note Information And Scale Diagrams For Guitarists



Diatonic Chords Exercises The Most Useful Important Jens Larsen
Diatonic means that the chords are made up from notes in the parent scale of the key so if a song is in the key of E major, say, then the majority of the notes in the melody will be found in the E major scale, and the notes that make up the supporting chords bar one or two exotic exceptions maybe will be taken from the E major scale tooStarting out (Holding, Left & Right Hand Position, Tuning) – Guitar Lesson 1;Melodic Minor Modes Melodic Minor;


Key Of G Major E Minor Freescaling Play To Learn



E Major Scale Guitar Ultimate Guide Guitar Lessons Blog
Melodic Minor Modes Melodic Minor;I IIm IIIm IV V VIm VIIdim C Major C Dm Em F G Am im F Major F Gm Am C Dm Edim Major Cm Dm Eb F Gm Adim Eb Major Eb Fm Gm Ab Cm Ddim Ab Major Ab m Cm Db Eb Fm Gdim Db Major Db Ebm Fm Gb Ab m Cdim Gb Major (F#) Gb (F#) Abm (G#m)Because we normally use chords with four or more notes in jazz, here are the diatonic chords in the key of C major with each chord being a fournote chord To help you understand these chords, try writing them out in various keys in order to memorize the order of diatonic fournote chords as applied to different root notes


The Six Diatonic Triads And The Diminished Triad Built On The Seven Download Scientific Diagram



Diatonic Chords Of E Major Scale Piano Music Theory
So the chords in E will root on the notes along the E major scale, since all chords in a major key are formed by notes from their respective diatonic scale The E major scale has 7 notes, each with a corresponding scale degree Degree 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 (octave) Note E F# G# A B C# D# EBasic folk guitar – Lesson 3;Which takes us to the chords that are using the language of your music And those chords are called "diatonic chords" Diatonic Chords The golden rule is to only use chords where all notes of the chord are within the scale and key of your music composition These chords are called "diatonic chords", which basically means Chords within



Creating Diatonic Jazz Chords And Melodies From Major Scales Guitar Kitchen


Unlocking The Mysteries Of Diatonic Harmony Art Of Composing
The major scale or Ionian mode is one of the diatonic scales It is made up of seven distinct notes, plus an eighth that duplicates the first an octave higher The pattern of seven intervals separating the eight notes is T–T–S–T–T–T–S In solfege, the syllables used to name each degree of the scale are Do–Re–Mi–Fa–Sol–La–Ti–DoA sequence of successive natural notesF Major (F) F – A – C;Diatonic means that the chords are made up from notes in the parent scale of the key so if a song is in the key of E major, say, then the majority of the notes in the melody will be found in the E major scale, and the notes that make up the supporting chords bar one or two exotic exceptions maybe will be taken from the E major scale too



Diatonic Chords Exercises The Most Useful Important Jens Larsen


Unlocking The Mysteries Of Diatonic Harmony Art Of Composing
Diatonic chords of each key center, it's great for practice scales patterns, improvisation and chords of cause!This is a characteristic of diatonic chords Every 7th diatonic chord in a Major key will be diminished So to recap All the diatonic chords in the key of C are C, Dm, Em, F, G, Am, im and back up to C at the top So there's a pattern here The 145 chords are all Major chords The 236 are all minor chords, and the 7 is a diminished chordBecause the chord types stay the same through all different keys, you can memorise them in a general form You should really learn this sequence by heart!


Jazz Comping In E Major


The E Major Scale
They are as follows Chord I E major Its notes are E – G# – B Chord ii F# minor Its notes are F# – A – C# Chord iii G# minor Its notes are G# – B – D# Chord IV A major Its notes are A – C# – E Chord V B majorOther Scales Harmonic Minor;Dorian (alternate) Mixolydian (alternate) Chord Progressions Major Diatonic Chords;



Soprano Recorder Scales E Major Diatonic Scale Diatonic Scale E Major Pentatonic Scale



Major Keys Diatonic Chords Triads Discover Guitar Online Learn To Play Guitar Music Theory Guitar Learn Guitar Chords Music Chords
The 7 Diatonic Triads are C Major (C) C – E – G;Chord Name 1st Note 2nd Note 3rd Note 4th Note 5th Note 6th Note Equal Chord1 Equal Chord2 Equal Chord3;Major Scale Modes Ionian;


Diatonic Seventh Chords Of Major Thecipher Com



Diatonic Chords Of A Flat Major Scale Piano Music Theory


Q Tbn And9gcr Hx9e42xzhzsgplnkrngbmsxkhavlb1ahkpeyjwqai Cg7lm Usqp Cau



Creating Diatonic Jazz Chords And Melodies From Major Scales Guitar Kitchen


Key Of E Major C Sharp Minor Freescaling Play To Learn



Diatonic Chords Of E Major Scale Piano Music Theory



15 Triads And Scales


The B Major Scale Notes Chords More



Chord Tensions Adding Colorful Notes To Chords Hub Guitar


When And How Are Modulations Diatonic Integral
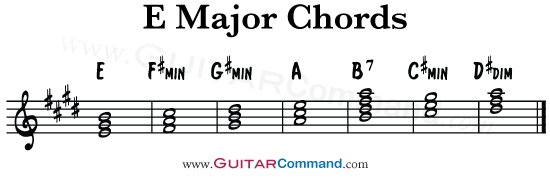


Chords In E Major Diatonic Guitar Command



Diatonic Chords Of E Major Scale Piano Music Theory



5 Most Used Chord Progressions In Edm Top Music Arts



Diatonic Chords Exercises The Most Useful Important Jens Larsen


Major Scale
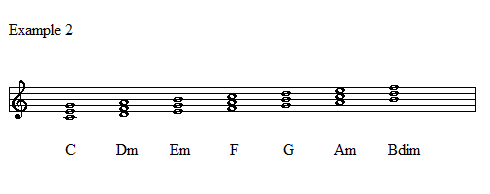


Diatonic Chords Guitar Noise


List Of All Major Scales With Notes Diatonic Triads Relative Minors Music Theory Site



E Major Scale Charts For Piano


How To Harmonize A Major Scale With 7th Chords Learn Jazz Standards



Major Scale Diatonic Chords Piano Music Theory



Do Major Triad Chord Notes Depend On The Key Key E Emaj Eg B Vs Key C Emaj Egb Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange



Major Scale Diatonic Chords Piano Music Theory



Basicmusictheory Com E Harmonic Minor 7th Chords



Discovering Minor Chord Progressions Musical U



What Is A Seventh Chord Building 4 Part Chords Hub Guitar



Understanding Diatonic Chord Progressions Triads And 7th Chords



Diatonic Triads


Diatonic Chords In Minor



Diatonic Chords Of E Major Scale Piano Music Theory



Are All Diatonic Chords In The Diminished Scale Diminished Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange


Diatonic Chords Guitar Noise



The Key Of E Major E Major Scale Key Signature Piano Chords And Common Chord Progressions Youtube


Triads And Seventh Chords Open Music Theory


Diatonic Chords In Minor



E Major Scale Charts For Banjo



Diatonic Chords Of D Major Scale Piano Music Theory



Diatonic Chords Of E Minor Scale Piano Music Theory



Diatonic Chords Triads And Sevenths In Every Major Key
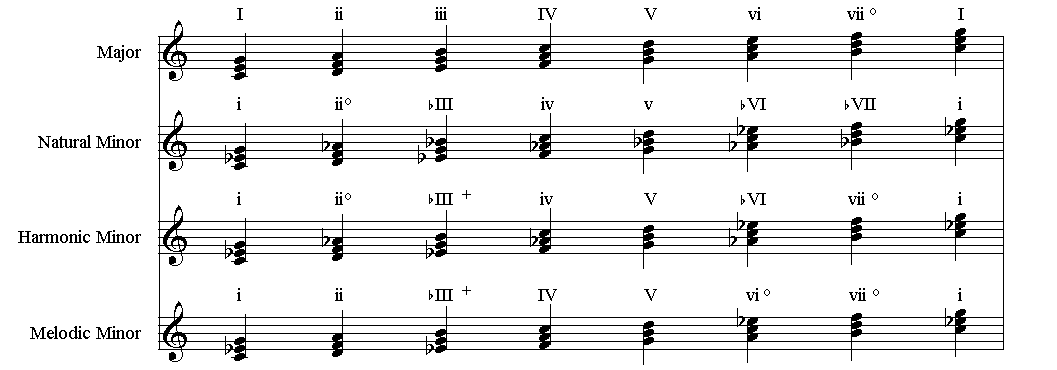


Dolmetsch Online Music Theory Online Triads Chords


Unlocking The Mysteries Of Diatonic Harmony Art Of Composing


1



C Major Scale Diatonic Chords Hd Png Download 1280x844 Png Dlf Pt


Diatonic Chords In Major Keys And The Harmonic System



What Are The Technical Names In Music What Do They Mean School Of Composition



E Major Scale Charts For Ukulele



Jazz School Major Scale Diatonic Seventh Chords Piano Ology


The E Major Scale


E Major Wikipedia


A Guide To Chromatic Chords Reverb Machine


Learn Major Scales Piano Treble Clef Charts Pattern Formula Chords Music Theory



Basicmusictheory Com E Harmonic Minor Chords


List Of All Major Scales With Notes Diatonic Triads Relative Minors Music Theory Site



Diatonic Chords Of G Minor Scale Piano Music Theory



Diatonic Chords Of E Flat Major Scale Piano Music Theory
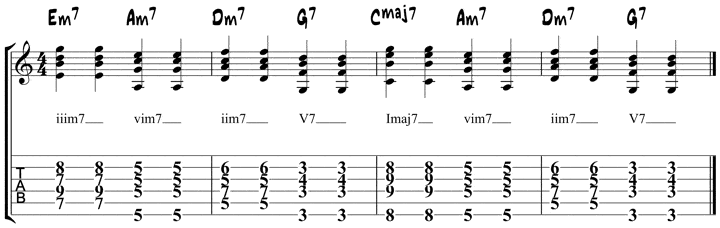


Diatonic Guitar Chords Chord Progressions



E Major Scale Charts For Guitar And Bass
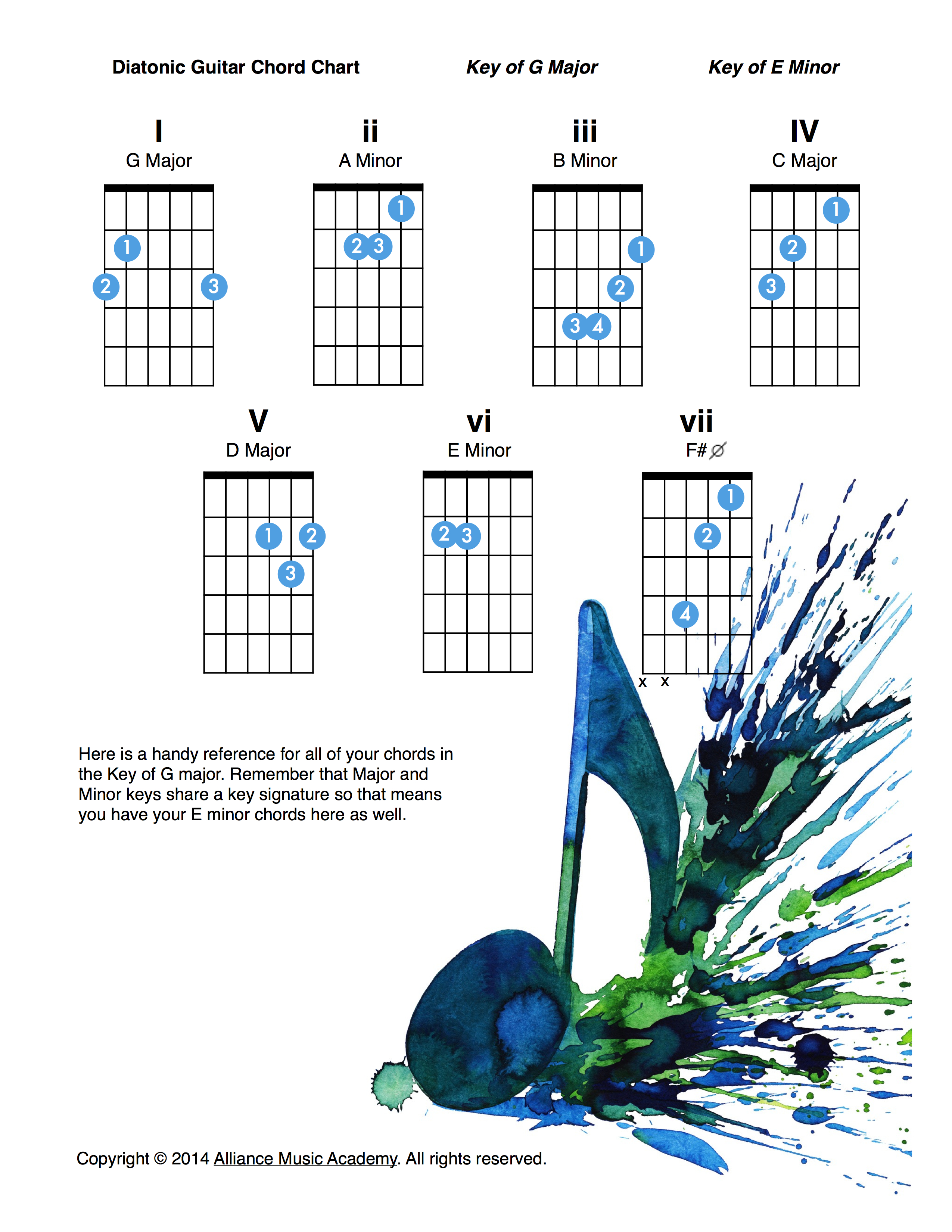


G Major Diatonic Guitar Chord Chart



E Major Scale Note Information And Scale Diagrams For Guitarists



Understanding Diatonic Chord Progressions Triads And 7th Chords


1



Diatonic Chords Of G Major Scale Piano Music Theory


Chords In The Key Of E


Using Extended Guitar Chords In A Progression


Q Tbn And9gcshzq3tpsoa86yvqors Sgozlxgwpxeayqptkubocn 9ixeiir Usqp Cau



コメント
コメントを投稿